
These findings suggest that the tsunamigenic potential of strike-slip faults is more important than previously thought, and should be taken into account for the re-evaluation of tsunami early-warning systems. Covered by the overlying cap rock and blocked by the lateral tight limestone, the unique fault-karst trap formed. Fractured-vuggy reservoirs formed along these faults after multiple periods of karstification. Waves propagating on two main branches reach highly populated sectors of the Iberian coast with maximum arrival heights of 6 m within 21 and 35 min, which is too quick for current early-warning systems to operate successfully. Abstract: A large number of strike-slip faults are developed in the Ordovician carbonate strata of Halahatang area in the northern Tarim basin.
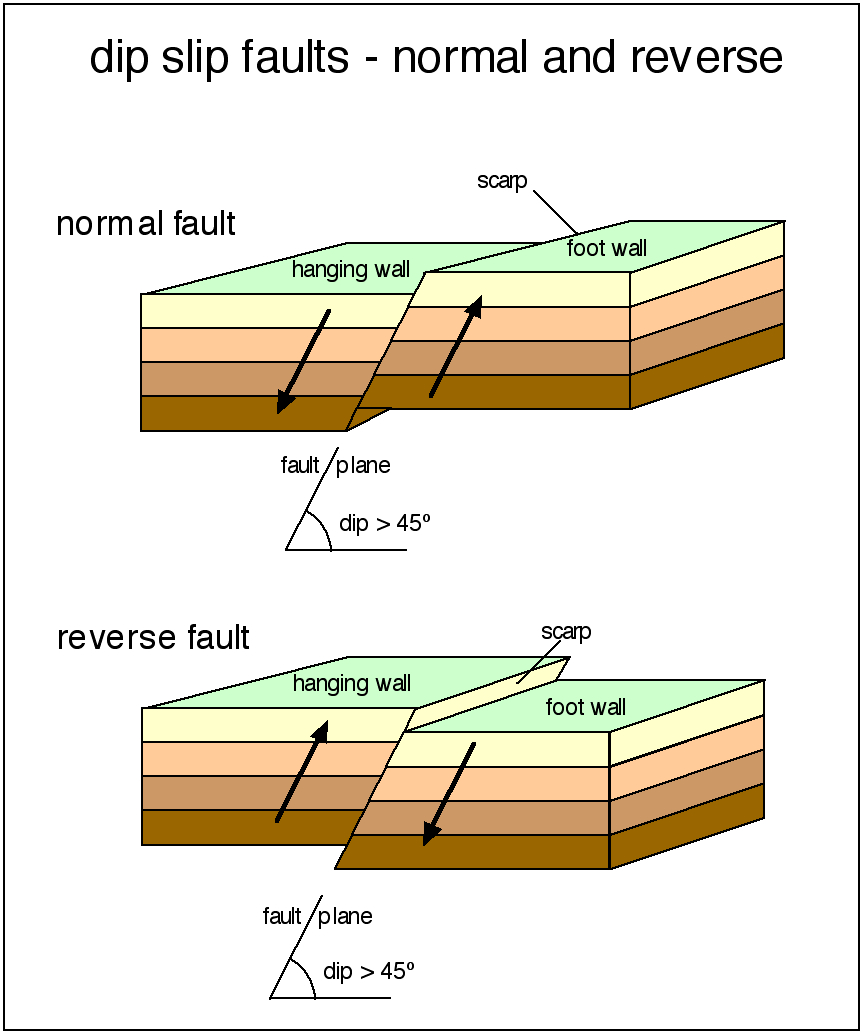
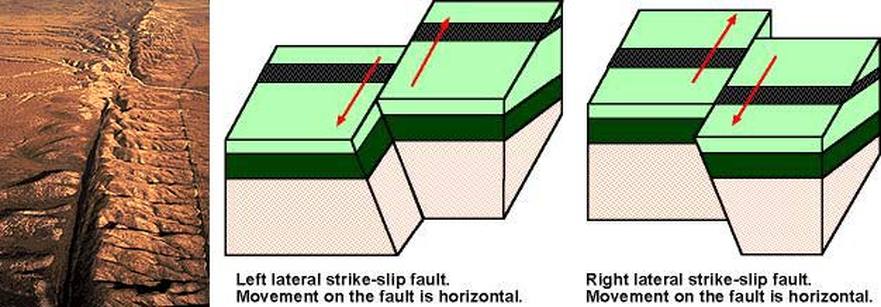
Physical modelling of strike-slip fault systems is a powerful and graphic. Strike-slip deformation typically results in complex vertical and horizontal sections that can be difficult to interpret coherently. The authors found the active dextral NW–SE Averroes Fault in the central Alboran Sea (westernmost Mediterranean) has a historical vertical throw of up to 5.4 m at its northwestern tip corresponding to an earthquake of Mw 7.0. Intraplate strike-slip zones commonly display intricate 3-D geometries, with rapid changes in structural style along strike and with depth. Nevertheless, strike-slip faults are usually disregarded as major triggers, as they are thought to be capable of generating only moderate seafloor deformation accordingly, the tsunamigenic potential of the vertical throw at the tips of strike-slip faults is not thought to be significant. The transform faults form plate boundaries connecting divergent (rift zones) or convergent margins (subduction zones). The fault plane is essentially vertical, and the relative slip is lateral along the plane. Tsunamis are triggered by sudden seafloor displacements, and usually originate from seismic activity at faults. This is an earthquake caused by a strike-slip fault. Strike-slip faults typical of planetary bodies interested by plate tectonics. Strike-slip (also called transcurrent, wrench, or lateral) faults are similarly caused by horizontal compression, but they release their energy by rock displacement in a horizontal direction almost parallel to the compressional force. Counterclockwise rotation or spiraling is also described as sinistral. If it moves to the right, the relative motion is described as dextral. The Shuntuo low uplift zone is a secondary structural unit in Tarim Basin, which is adjacent to Manjiaer Sag and Awati sag in East and West and is clamped by Tabei uplift and Tazhong uplift in north and south (Fig.
Strike slip fault software#
In this publication, the authors modelled the tsunamigenic potential of this seafloor deformation by Tsunami-HySEA software using the Coulomb 3.3 code. Geology Pertaining to a strike - slip or left- lateral fault in which the block across the fault moves to the left also called a sinistral strike-slip fault.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
